Deliberative Democracy and the Ethical Challenges of Generative AI
Introduction
Generative AI has become an incredibly attractive and widespread tool for people across the world. Alongside its rapid growth, AI tools present a host of ethical challenges relating to consent, security, and privacy, among others. As Generative AI has been spearheaded primarily by large technology companies, these ethical challenges — especially as viewed from the vantage point of ordinary people — risk being overlooked for the sake of market competition and profit. What is needed, therefore, is a deeper understanding of and attention to how ordinary people perceive AI, including its costs and benefits.
The Meta Community Forum Results Analysis, authored by Samuel Chang, James S. Fishkin, Ricky Hernandez Marquez, Ayushi Kadakia, Alice Siu, and Robert Taylor, aims to address some of these challenges. A partnership between CDDRL’s Deliberative Democracy Lab and Meta, the forum enables participants to learn about and collectively reflect on AI. The impulse behind deliberative democracy is straightforward: people affected by some policy or program should have the right to communicate about its contents and to understand the reasons for its adoption. As Generative AI and the companies that produce it become increasingly powerful, democratic input becomes even more essential to ensure their accountability.
Motivation & Takeaways
In October 2024, the third Meta Community Forum took place. Its importance derives from the advancements in Generative AI since October 2023, when the last round of deliberations was held. One such advancement is the move beyond AI chatbots to AI agents, which can solve more complex tasks and adapt in real-time to improve responses. A second advancement is that AI has become multimodal, moving beyond the generation of text and into images, video, and audio. These advancements raise new questions and challenges. As such, the third forum provided participants with the opportunity to deliberate on a range of policy proposals, organized around two key themes: how AI agents should interact with users and how they should provide proactive and personalized experiences for them.
To summarize some of the forum’s core findings: the majority of participants value transparency and consent in their interactions with AI agents as well as the security and privacy of their data. In turn, they are less comfortable with agents autonomously completing tasks if this is not transparent to them. Participants have a positive outlook on AI agents but want to have control over their interactions. Regarding the deliberations themselves, participants rated the forum highly and felt that it exposed them to alternative perspectives. The deliberators wanted to learn more about AI for themselves, which was evidenced by their increased use of these tools after the deliberations. Future reports will explore the reasoning and arguments that they used while deliberating.
The participants of this Community Forum were representative samples of the general population from five countries - Turkey, Saudi Arabia, India, Nigeria, and South Africa. Participants from each country deliberated separately in English, Hindi, Turkish, or Arabic.
Methodology & Data
The deliberations involved around 900 participants from five countries: India, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, and Turkey. Participants varied in terms of age, gender, education, and urbanicity. Because the deliberative groups were recruited independently, the forum can be seen as five independent deliberations. Deliberations alternated between small group discussions and ‘plenary sessions,’ where experts answered questions drawn from the small groups. There were around 1000 participants in the control group, who did pre- and post-surveys, but without deliberating. The participant sample was representative with respect to gender, while the treatment and control groups were balanced on demography as well as on their attitudes toward AI. Before deliberating on the proposals, participants were presented with background materials as well as a list of costs and benefits to consider.
In terms of the survey data, large majorities of participants had previously used AI. There was a statistically significant increase in these proportions after the forum. For example, in Turkey, usage rates increased from nearly 70% to 84%. In several countries, there were large increases in participants’ sense of AI’s positive benefits after deliberating, as well as a statistically significant increase in their interest. The deliberations changed participants’ opinions about a host of claims; for example, “people will feel less lonely with AI” and “more proactive [agents] are intrusive” lost approval whereas “AI agents’ capability to increase efficiency…is saving many companies a lot of time and resources” and “AI agents are helping people become more creative” gained approval. After deliberating, participants demonstrated an improved understanding of some factual aspects of AI, although the more technical aspects of this remain challenging. One example here is AI hallucinations, or rather, the generation of false or nonsensical outputs, usually because of flawed training data.
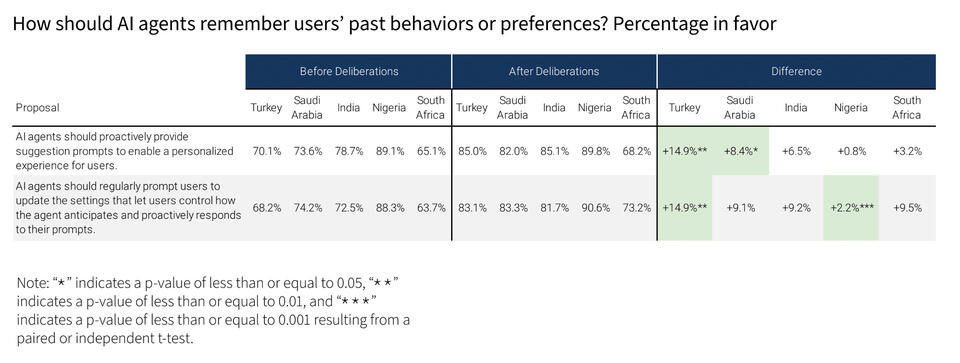
Proposals
Participants deliberated on nineteen policy proposals. To summarize these briefly: In terms of whether and how AI remembers users’ past behaviors and preferences, participants preferred proposals that allowed users to make active choices, as opposed to this being a default setting or only being asked once. They also preferred being reminded about the ability of AI agents to personalize their experience, as well as agents being transparent with users about the tasks they complete. Participants preferred that users be educated on AI before using it, as well as being informed when AI is picking up on certain emotional cues and responding in “human-like” ways. They also preferred proposals whereby AI would ask clarifying questions before generating output. Finally, when it comes to agents helping users with real-life relationships, this was seen as more permissible when the other person was informed. Across the proposals, gender was neither a significant nor consistent determinant of how they were rated. Ultimately, the Meta Community Forum offers a model for how informed, public communication can shape AI and the ethical challenges it raises.
*Research-in-Brief prepared by Adam Fefer.

CDDRL Research-in-Brief [4-minute read]










