Climate Change and Mental Health Among Teenagers in Two Bangladeshi Cities
Motivation & Overview:
The effects of the climate crisis are thought to be extremely far-reaching, from declining economic growth and agricultural productivity to housing displacement and job loss. An important set of consequences are psychological, relating to how climate change can exacerbate anxiety and one’s sense of hopelessness about an uninhabitable future. These psychological impacts are heightened for members of vulnerable and marginalized groups, as well as for those in poor and underdeveloped places that struggle to address climate change.
In “Adolescent psychological health, temporal discounting, and climate distress under increased flood exposure in Bangladesh,” Liza Goldberg and her coauthors examine the psychological well-being of 15 to 18-year-olds in two Bangladeshi cities that have been differentially affected by floods. The authors conduct surveys and focus groups with adolescents in the low-flood-risk capital city of Dhaka and the high-flood-risk city of Barisal. They find that although adolescents in both cities fear the personal impacts of climate change, rates of anxiety and depression are significantly higher in Barisal. In addition, those with anxiety and depression exhibit greater temporal discounting, meaning that short-term consequences are favored over longer-term ones. Discounting is an important — if neglected — consequence because adolescents will emerge as household decision-makers who must plan to adapt to climate change. The article is notable in increasing our knowledge of how floods harm members of an already vulnerable population.
Case Selection and Hypotheses:
Bangladesh is among the world’s most climate-vulnerable countries. This is due to its “deltaic” geography (i.e., its low, flat land, crossed by many rivers) and consequent flood exposure, extreme temperature and humidity, and poor air quality. Barisal — a city of over 500,000 that is roughly 115 kilometers from Dhaka — is highly vulnerable to flooding, as well as being poorer (relative to Dhaka) and limited in its “climate adaptation infrastructure.” Partly for these reasons, rates of migration from Barisal to Dhaka are the highest in Bangladesh. By contrast, Dhaka — the capital city of over 24 million — is less flood-exposed and is slightly wealthier. Respondents in Barisal and Dhaka reported around four floods and one flood per year, respectively.
Figure. Study site locations in Bangladesh. Study sites at Dhaka (A) and Barisal (B) are shown in red.
The authors hypothesize that Barisal’s greater flood exposure would be associated with more anxiety and depression among its adolescents, and that anxiety and depression would be associated with greater temporal discounting. (In other words, they do not expect that flood exposure would be directly associated with discounting.) In addition, the authors expect that these negative psychological effects would be especially pronounced among poor Bangladeshis, girls, and those with a greater awareness of the climate crisis.
Data and Findings:
The authors surveyed 1200 Bangladeshi adolescents in 24 schools immediately after the flood season, which usually runs from May to September. In addition, 16 focus groups were conducted with around 160 total participants. Adolescents in both cities expressed a high familiarity with climate change. However, and consistent with the authors’ expectations, those in Barisal expressed significantly higher levels of agreement with statements about climate distress. For example 97% of those in Barisal compared to just 68% in Dhaka agreed that “My family’s security will be threatened,” 93% in Barisal and 58% in Dhaka agreed that “The things I most value will be destroyed,” and 98% in Barisal and 67% in Dhaka agreed that “My feelings about climate change negatively affect my daily life.”
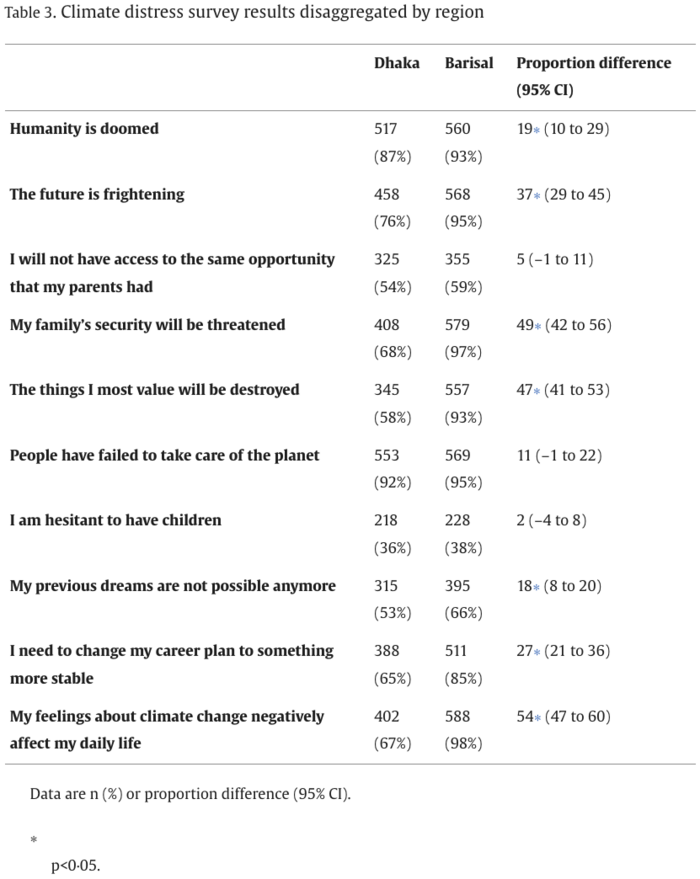
Table 3. Climate distress survey results disaggregated by region.
The focus groups corroborated this unequal sense of despair, especially concerning the future and one’s educational and career goals. In Barisal, a boy said, “We expect that we will have to continue withstanding this [flooding] for many years to come,” while a girl said, “I used to want to become a teacher myself, but now I believe I will need to get married immediately after school because my father keeps losing his job during the floods.” By contrast, and because flooding in Dhaka is so infrequent, adolescents did not expect climate change to meaningfully threaten their life trajectories.
In terms of anxiety and depression, 86% of those in Barisal reported anxiety symptoms, compared to 71% in Dhaka, while 98% in Barisal and 88% in Dhaka reported depressive symptoms. After adjusting for factors like sex, wealth, and climate change awareness, the odds of being anxious and depressed in Barisal were nearly twice as high and more than 3.5 times as high, respectively. Across both cities, females were more than 1.75 times as likely to experience anxiety. And the odds of being depressed were over 1.85 times as high for those with a greater awareness of climate change.
Girls in the Barisal focus groups revealed that flooding was linked to domestic violence. Fathers facing financial insecurity were reported to engage in violence against their mothers as a consequence of this stress. As one girl put it, “The floods keep getting worse and worse. So, I may experience even more violence than my mother does.” By contrast, few girls in Dhaka expressed worsening family dynamics, and none reported domestic violence owing to flooding. Adolescents in Dhaka believed that floods in their region were simply too fleeting to result in such abuse.
Finally, only 7% and 6% of adolescents in Barisal and Dhaka showed signs of temporal discounting. However, the odds of discounting were twice as high for those with anxiety and almost 2.5 times as high for those with depression. The authors find some evidence of discounting in the focus groups, but no meaningful differences across cities. This absence may be due to discounting behaviors emerging around adulthood, which is older than the adolescent study population. Taken together, the authors’ findings imply that mental health support will be essential for those affected by climate change — especially in impoverished areas — to help them manage stress and to improve their ability to plan for the future.
*Research-in-Brief prepared by Adam Fefer.

CDDRL Research-in-Brief [4-minute read]







