New Data on Biographic and Demographic Attributes of Legislators
New Data on Biographic and Demographic Attributes of Legislators
CDDRL Research-in-Brief [3.5-minute read]

Introduction and Motivation:
Social scientists and philosophers have shown increased interest in the concept of descriptive representation. Indeed, the identities and life experiences of those doing the representing may be critical for enacting the preferences of those being represented. This is especially the case for historically marginalized groups — upper-class, educated men may simply fail to adequately represent lower-class, uneducated, or women voters. In addition to considerations of fairness, there is growing recognition that descriptive representation can improve policy outcomes, such as service delivery or trust in government.
However, the study of descriptive representation has been hampered by data availability. Identifying simple correlations across the world’s democracies — for example, between proportions of working-class legislators and levels of social welfare provision — has hitherto been impossible.
In “The Global Legislators Database,” Nicholas Carnes, Joshua Ferrer, Miriam Golden, Esme Lillywhite, Noam Lupu, and Eugenia Nazrullaeva introduce the largest dataset of biographic and demographic information on national legislators ever assembled. GLD will enable scholars to assess just how much voters elect those with life experiences resembling their own. The authors compile information on five descriptive variables across 97 democracies: legislators’ party affiliation, gender, age, highest level of education, and previous occupation (to assess their social class). By contrast, prior datasets have focused only on heads of state or cabinet members, or on only a selection of more developed democracies.
Some questions around descriptive representation would seem to have intuitive answers: Wouldn’t developed countries have more women representatives, or wouldn’t women legislators feature less prominently in right-wing parties? Scholars can now hope to do more than merely gesture at answers.
Characteristics, Validity Checks, and Applications:
GLD comprises countries that (a) have a population of over 300,000 and (b) meet the standard for what Freedom House calls “Electoral Democracy” — having some minimum of political rights and civil liberties. Excluding six cases of data availability constraints, this yields 97 countries, including India, the United States, Brazil, Mexico, Nigeria, and the Philippines. Scholars of Pakistan, Bangladesh, or Turkey — who would likely characterize these countries as authoritarian during the 2015-17 time period — will be pleased that the authors chose a more forgiving measure of democracy.
Biographic data is drawn from the national legislature in unicameral countries and the lower chamber in bicameral countries. (By contrast, upper chambers are sometimes indirectly appointed or hereditary, which sheds less light on whether voters choose descriptively similar representatives.) This yields over 19,000 individuals who held office during at least one legislative session in 2015, 2016, and 2017. GLD has remarkably complete data for the five variables mentioned above: age and education data are presented for over 90% of legislators in the dataset, for over 93% as regards occupation, and nearly 100% for gender.
In order to assess GLD’s validity, the authors compare select variables to those in comparable datasets. For example, the gender variable is compared with gender data from the Varieties of Democracy (V-Dem) project, which shows that the two measures are nearly identical. So too is the age data nearly identical to an index from 15 affluent democracies.
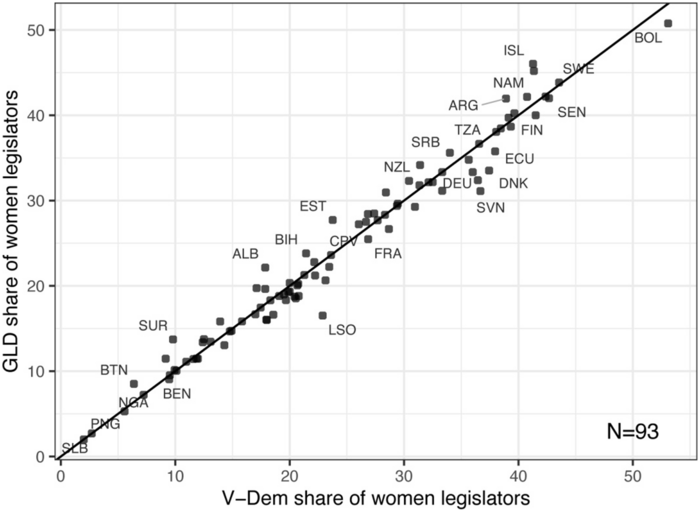
Figure 1. Shares of women legislators in the GLD and V-Dem. Note: Bahamas, Belize, Fiji, and Kosovo are omitted because of missing data in the V-Dem.
For categories like education and prior occupation — where comparable data are unavailable — the authors conduct “face validity” tests: these draw on our intuitions that legislators are, for example, mostly educated and not working class. And indeed, these intuitions are borne out in the distributions of GLD data. In terms of total coverage, GLD includes information on more legislators than the comparable Global Leadership Project database for all but two countries, and in many cases, the differences are large.
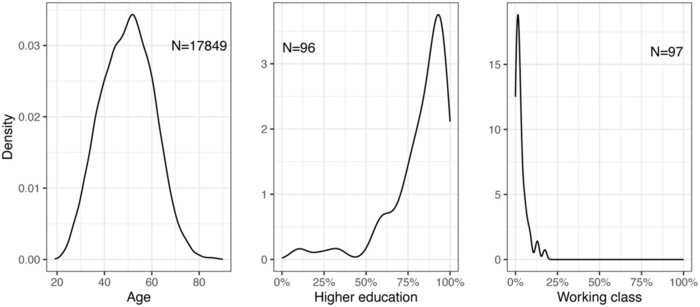
Figure 3. Distributions of legislator traits in the GLD. Note: Age is calculated at the time of election. Higher education includes levels beyond primary and secondary education (Bachelors, Masters, PhD, LLB, LLM, JD, MD, and short-cycle tertiary). Data on educational attainments for legislators is unavailable for Côte d’Ivoire.
The authors then use GLD in application to a number of questions for which scholars have lacked global data. First, some have hypothesized that in legislatures with more (a) uneducated, (b) female, and (c) working-class representatives, incumbency rates will be lower. This is because individuals from these three groups might have a harder time overcoming challenges relating to expertise, sexism, and fundraising, respectively. Correlating GLD data with a global reelection database, the authors find only evidence for (b), suggesting that women may face higher barriers to remaining in office. These are only correlations, but they point to fruitful areas for exploration: why might women face unique barriers, and what distinguishes countries with lower versus higher barriers?
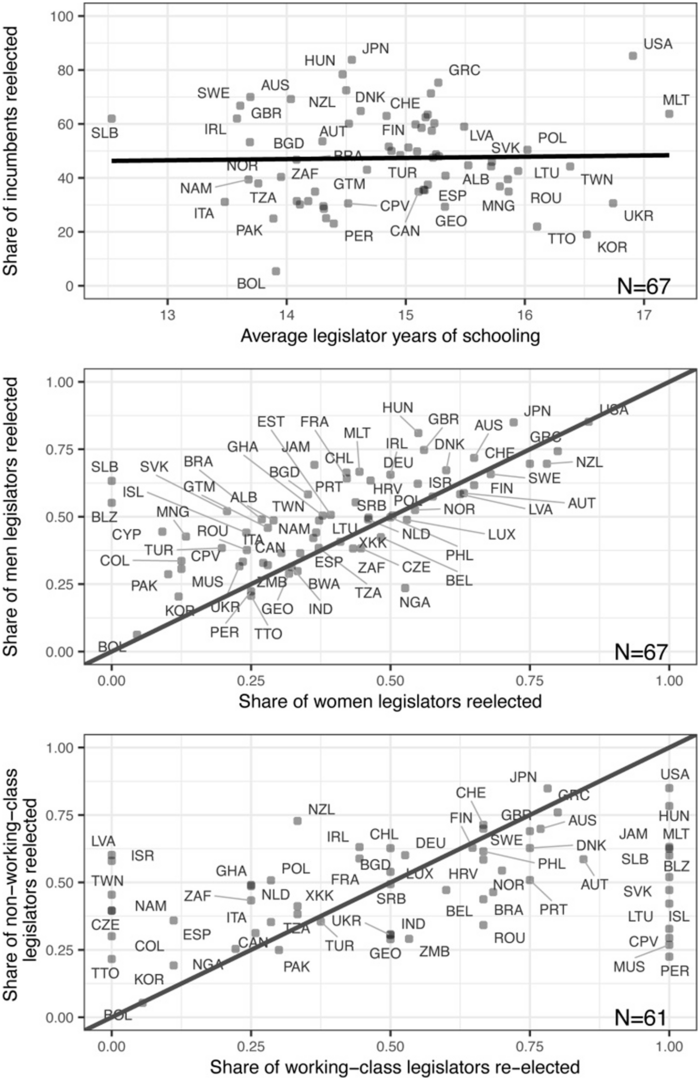
Figure 5. Re-election rates by years of education, gender, and occupational background. Note: The share of working-class legislators is zero for six countries that are dropped from the figure: Albania, Botswana, Cyprus, Estonia, Guatemala, and Mongolia.
A second application involves public financing of elections, which is thought to favor more working-class legislators who would have a harder time fundraising. Correlating V-Dem data on public financing with the GLD variable on prior occupation, however, the authors find limited evidence for this conjecture. Finally, some have proposed that countries with a stronger rule of law would favor a higher proportion of lawyers in the national legislature. Looking again at GLD prior occupation data alongside V-Dem rule of law data, the authors find limited evidence for this hypothesis.
These varied applications point to how the Global Legislators Database can serve as a valuable resource for scholars interested in the causes and consequences of descriptive representation. Although the GLD covers only a single point in time, it can serve as a bedrock for additional data-collection efforts. In addition to expanding its temporal coverage, scholars may also wish to gather data on upper chambers. Especially in ethnically diverse countries like Bosnia and Herzegovina, upper chambers are intended to mirror the descriptive composition of specific regions. However, it may be the case that ethnic representatives are still vastly more wealthy or educated than their constituents, thus impeding their ability to represent.
*Brief prepared by Adam Fefer.
